Find out in this video!Next video on voltage http//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=TBtkxYfyncWebsite http//wwwafroteAlternating Current (AC) — An electric current that reverses its direction many times a second at regular intervals Ammeter — An instrument for measuring the flow of electrical current in amperes Ammeters are always connected in series with the circuit to be testedMeaning of Resistance Resistance may be defined as that property of a substance which opposes (or restricts) the flow of an electric current (or electrons) through it The practical as well as mks (or SI) unit of resistance is ohm (Ω), which is defined as that resistance between two points of a conductor when a potential difference of one

11 2 Ohm S Law Electric Circuits Siyavula
What is this symbol ω
What is this symbol ω-Current is the rate of flow of electric charge A potential difference (voltage) across an electrical component is needed to make a current flow through it Resistance = 240 ÷ 3 = 80 Ω The Power Ministry is likely to add 76,000 MW of power in the 12th Five Year Plan Period (1217) One may also ask, what are the units of electricity?
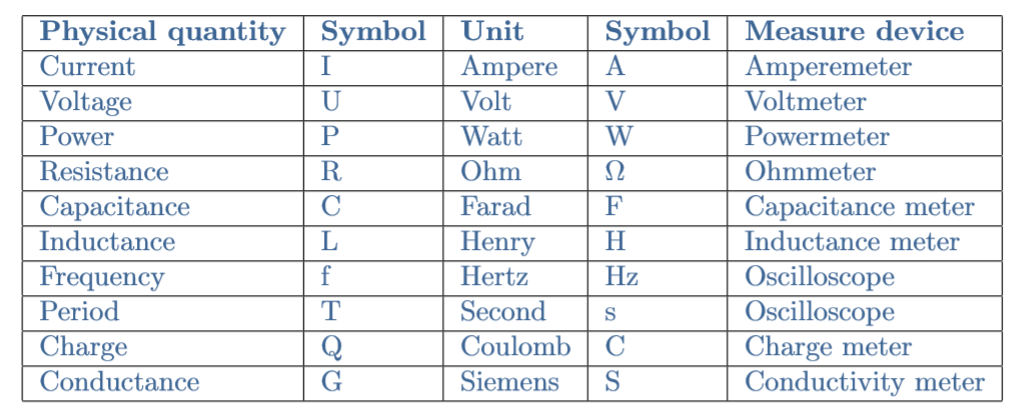



Electrical Units Of Measure Electronics Lab Com
Indicate that each turn around the spiral represents an integer power of ω it represents the space of the differential forms For example, "A differential kform ω is called closed if its outer differential is zero, that is, dω = 0" In telecommunications, it is related to the spectrum of the continuous signal Ω=𝜌 𝑔 𝑄 𝑆 (1) where Ω is stream power, ρ is the density of water (1,000 kg/m3 at 4 C), g is gravity (98 m/s2), Q is river discharge, and S is energy gradient, which is equivalent to channel slope in uniform flow Bagnold also defined the "mean available power supply to the column of fluid over unit bed area," 𝜔=Ω / (2)Omega The 24th and last letter of the Greek alphabet Commonly used to make things sound mysteriously powerful and amazing The symbol can be created by holding the ALT key and pressing 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, and 0 on the number pad Contrast alpha
From Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English Related topics Electrical, Electricity, Electricity electricity e‧lec‧tri‧ci‧ty / ɪˌlekˈtrɪsəti, ˌelɪk/ S2 W3 noun uncountable 1 TEE the power that is carried by wires, cable s etc, and is used to provide light or heat, to make machines work etc The farm was very isolated, but it had electricity 2 EXCITED a feeling of = Iwire (A) × (2 × L(ft) × Rwire(Ω/kft) / 1000(ft/kft)) The voltage drop V in volts (V) is equal to the wire current I in amps (A) times 2 times one way wire length L in meters (m) times the wire resistance per 1000 meters R in ohms (Ω/km) divided by 1000 Vdrop (V) = Iwire (A) × Rwire(Ω) = Iwire (A) × (2 × L(m) × Rwire (Ω/km) / 1000(m/km))Information and translations of electricity in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web
The ohm is the resistance between two points of an electrical conductor transmitting a current of one ampere when the potential difference is one volt The ohm is the SI derived unit for electrical resistance in the metric system Ohms can be abbreviated as Ω;It used to be onetenth of the unit of electric current in centimetre – gram – second system of units Now, those units are called abampere, which is defined as the amount of current that produces a force of two dynes per centimetre of length in between two wires that areThe resistance R in ohms (Ω) is equal to the voltage V in volts (V) divided by the current I in amps (A) The resistance R in ohms (Ω) is equal to the squared voltage V in volts (V) divided by the power P in watts (W) The resistance R in ohms (Ω) is equal to the power P in watts (W) divided by the squared current I in amps (A)
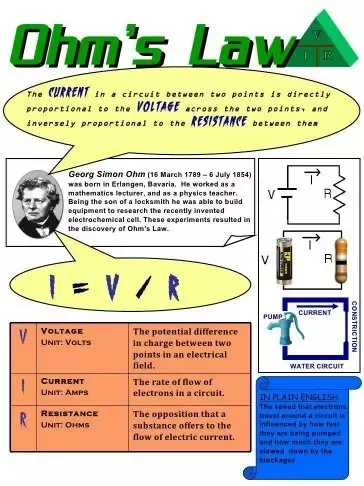



Do Transformers Obey Ohm S Law If Yes How Quora



Electrical Units And Metric Prefixes Examples
When this electrical appliance is connected to a 230 Ω supply line, the current passing through it will be a) 092A b) 29A c) 92A d) 92A Answer The correct option is c) 92A Q24 When a 4 Ω resistor is connected across the terminals of a 12V battery, the number of coulombs passing through the resistor per second is a) 03 b) 3 cOhm's Law Calculator – Power, Current, Voltage & Resistance Calculator Below are the four Electrical calculators based on Ohm's Law with Electrical Formulas and Equations of Power, Current, Voltage and Resistance in AC and DC Single phase & Three Phase circuit Enter the known values and select a conversion from the buttons below and click on Calculate result will displayTherefore, the power consumed by the 2 Ω is 8 W (ii) When 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors are connected in parallel, the voltage across the resistors remains the same Knowing that the voltage across 2 Ω resistor is 4 V, we can calculate the power consumed by the resistor as follows The power consumed by the 2 Ω resistor is 8 W 15
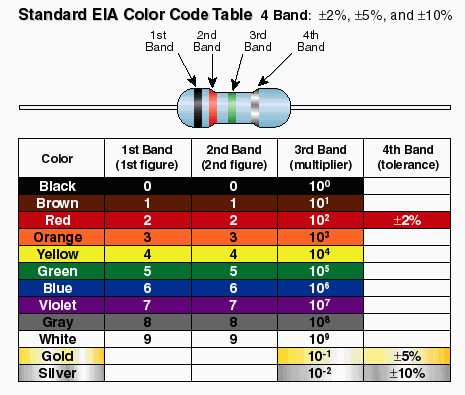



Resistance Ohm S Law What Is Electrical Resistance Tecnologia Eso En Ingles




Ohm S Law Again Electrical Safety Electronics Textbook
A form of energy, of unknown nature, the cause of manifold "electrical" phenomenalight, heat, attraction, repulsion, etc Two forms are distinguishedresting or static e, and flowing, current, or dynamic e;2) what is mean by dynamic power 300W Front at 3 Ohm? Electrical gadgets of different powers need different currents for their proper functioning This means the current drawn by an appliance depends on its power A bulb of 10 Ω and a heater of 100 Ω cannot work properly when same current flows through each of them The bulb needs smaller current while the heater requires larger current




11 2 Ohm S Law Electric Circuits Siyavula
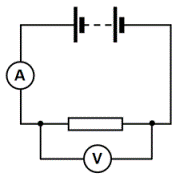



Episode 108 Resistance Iopspark
Resistance is a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit Resistance is measured in ohms, symbolized by the Greek letter omega (Ω) Ohms are named after Georg Simon Ohm (), a German physicist who studied the relationship between voltage, current and resistance He is credited for formulating Ohm's Law A free online environment where users can create, edit, and share electrical schematics, or convert between popular file formats like Eagle, Altium, and OrCAD Transform your product pages with embeddable schematic, simulation, and 3D content modules while providing interactive user experiences for your customersThe ohm (symbol Ω) is the SI derived unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Ohm
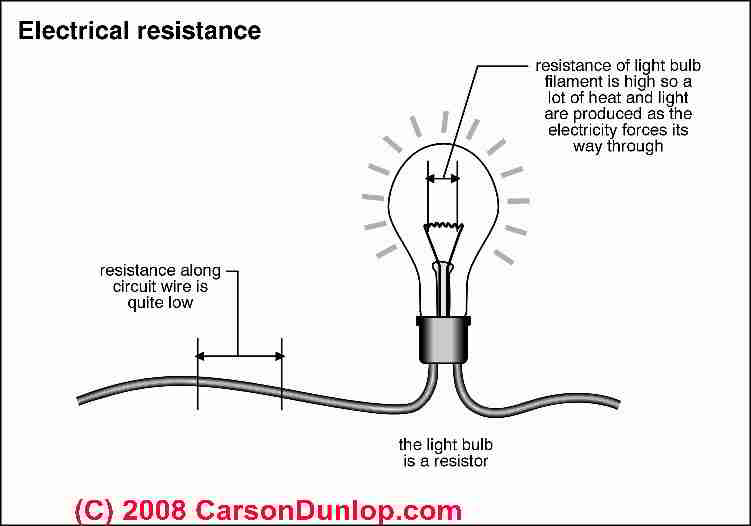



Definition Of Ohm S Law Explanation Measurement Of Electrical Resistance



How Voltage Current And Resistance Relate Ohm S Law
PHY54 Chapter 21 19 Power in AC Circuits ÎPower formula ÎRewrite using Îcosφis the "power factor" To maximize power delivered to circuit ⇒make φclose to zero Max power delivered to load happens at resonance Eg, too much inductive reactance (X L) can be cancelled by increasing X C (eg, circuits with large motors) 2 P ave rms=IR rms ave rms rms rms cosWatt definition Watt is the unit of power (symbol W) The watt unit is named after James Watt, the inventor of the steam engine One watt is defined as the energy consumption rate of one joule per second 1W = 1J / 1s One watt is also defined as theTable 1 Electrical Units, Symbols, and Definition In certain circuit applications the basic electrical units—volt, ampere, ohm, and watt—are either too small or too big to express conveniently In such cases metric prefixes are often used Recognizing the meaning of a prefix reduces the possibility of confusion in interpreting data
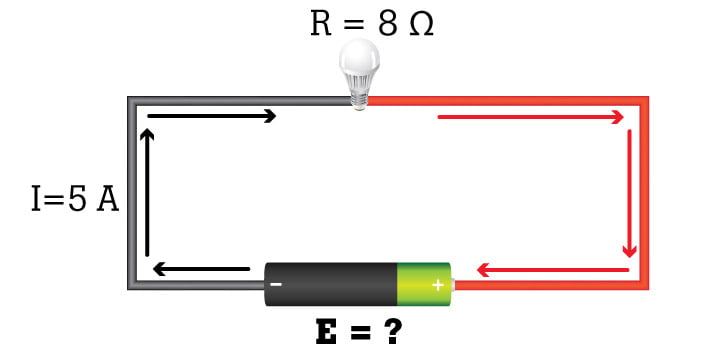



What Is Ohm S Law Fluke




Voltage What Is It Definition Formula And How To Measure Potential Difference Electrical4u
Looking for the definition of Ω?It is produced by friction, chemical action, or induction Electricity is positive or vitreous, that produced by rubbing glass with silkIn this chapter we will go through 1 Series Circuits 2 Voltage Divider Rule 3 Applied Voltage 4 Kirchoff's Voltage Law 5 Power in Series Circuit 6 Effects of Open in Series Circuit 7 Effects of Close in Series Circuit




Ohm S Law Definition History Formula Faq Sitename
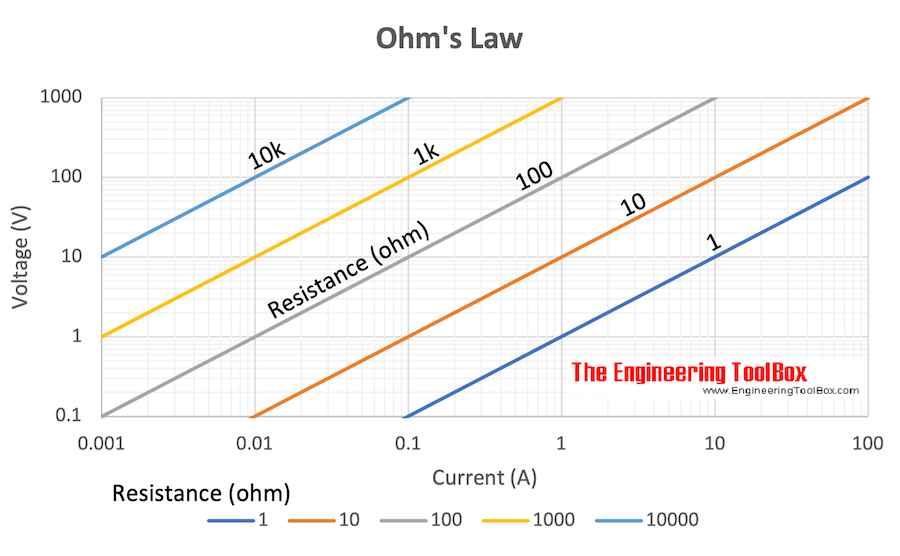



Electrical Formulas
R – Resistance, measured and expressed in ohms (Ω) RF – Radio Frequency, describing the rate of oscillation;The standard units of electrical measurement used for the expression of voltage, current and resistance are the Volt V , Ampere A and Ohm Ω respectively These electrical units of measurement are based on the International (metric) System, also known as the SI System with other commonly used electrical units being derived from SI base units Reactive Power — Reactive power is the portion of electricity that establishes and sustains the electric and magnetic fields of AC equipment Exists in an AC circuit when the current and voltage are not in phase Measured in VARS Resistance (Ω Ohms) — The opposition to the passage of an electric current Electrical resistance can be




Resistors And Ohm S Law Ppt Download




Omega Symbol Sign And It S Meaning Greek Alphabet W W Ohm Symbol
Find out what is the full meaning of Ω on Abbreviationscom! The SI unit for a resistor (the electrical resistance is measured in) Ohm and is represented as Ω The unit ohm (Ω) is named honor of the great German physicist and mathematician Georg Simon Ohm In SI system, an ohm is equal to a 1 volt per ampereFor example, 1 ohm



1




Understanding The Basics Of Electricity By Thinking Of It As Water
Ohmic materials have a resistance R that is independent of voltage V and current I An object that has simple resistance is called a resistor, even if its resistance is small The unit for resistance is an ohm and is given the symbol Ω (upper case Greek omega)What is electrical current?Watt W = J/s = m 2 kg/s 3 Quantity of electricity, electric charge / elektrische Ladung coulomb C = s A Electric potential / elektrische Spannung volt V = W/A = m 2 kg/s 3 A Capacitance / Kapazität farad F = C/V = s 4 A 2 /m 2 kg Electric resistance / elektrischer Widerstand ohm Ω = V/A = m 2 kg/s 3 A 2




Omega Symbol W W Definition In Word Excel Alt Code Mac




11 2 Ohm S Law Electric Circuits Siyavula
Are they giving 300W per speaker at Left , Center and Right?'angular velocity' is one option get in to view more @ The Web's largest and most authoritative acronyms and abbreviations resourceEnergy/Electricity and its units A unit (as mentioned on the electricity bills) is represented in kWH or Kilowatt Hour This is the actual electricity or energy used




Electrical Units Of Measure Electronics Lab Com
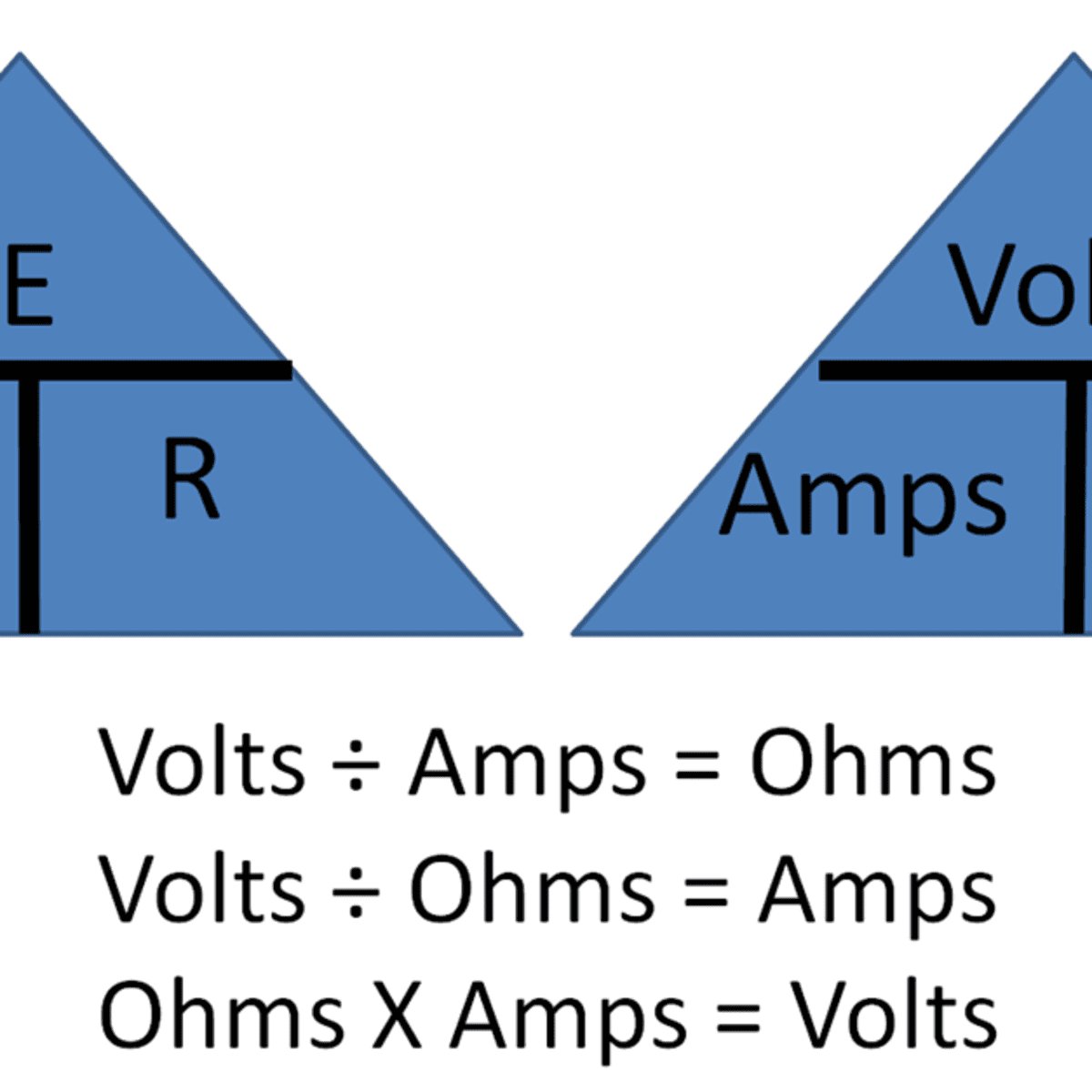



Using Ohm S Law In Basic Electrical And Electronics Testing In Vehicles Axleaddict
SW – Short Wave or Shortwave, as in the case with shortwave bands and shortwave radio;Definition of electricity in the Definitionsnet dictionary Meaning of electricity What does electricity mean?Plain language definitions of electrical terms Definition of amps, volts, watts, resistance, current, ohms, electrical phases We include basic formulas relating amps, volts, resistance, watts, and we explain what these electrical terms mean in practical applications such as for building or appliance electrical power, electrical wiring, and basic troubleshooting




Definition Of Ohm S Law Chegg Com




What Is An Ohm With Pictures
The uppercase Omega sign/symbol is used in chemistry to represent the stable natural oxygen isotope called oxygen18 In physics, the symbol represents ohm, a unit used to measure electrical resistance In cosmology (astronomy) it isElectronics for Absolute Beginners, Chapter 3 Welcome to Chapter 3!What do they mean by 185W at 1% THD 1 chnl driven, IEC and yet 230W / ch with some JEITA?
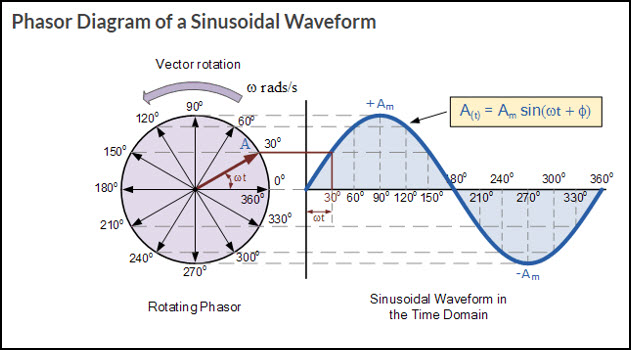



Relation Of Radians Angular Velocity To Ac Gbc Electronics Technician




Getting Started With Your Multimeter Make
Dynamic Power 300 W (3 Ω, Front) 250 W (4 Ω, Front) 150 W (8 Ω, Front) ===== 1) exactly WHAT is the output wattage per channel?Power W watt ω, ω rotational velocity, rotational speed rad/s radian per second α, α rotational acceleration rad/s 2 radian per second squared τ, τ torque N m newton meter I moment of inertia kg m 2 kilogram meter squared L, L angular momentum kg m 2 /s kilogram meter squared per second H, H angular impulse N m s newton meter second k spring constant N/m newtonV – Voltage/Volt, a unit of electromotive force;
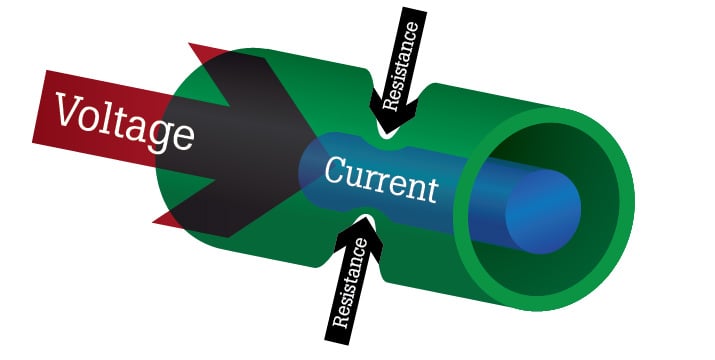



What Is Resistance Fluke




Ohm S Law Definition Formula Applications Of Ohm S Law Videos
ELECTRICITY ELECTRIC CURRENT If the electric charge flows through a conductor (for example, through a metallic wire), we say that there is an electric current in the conductor Definition Electric current is defined as the rate of flow of charge flowing through a crosssection of a wire/conductor Formula If a net charge Q, flows across any crosssection of aVA – VoltAmpere, a unit of electrical power
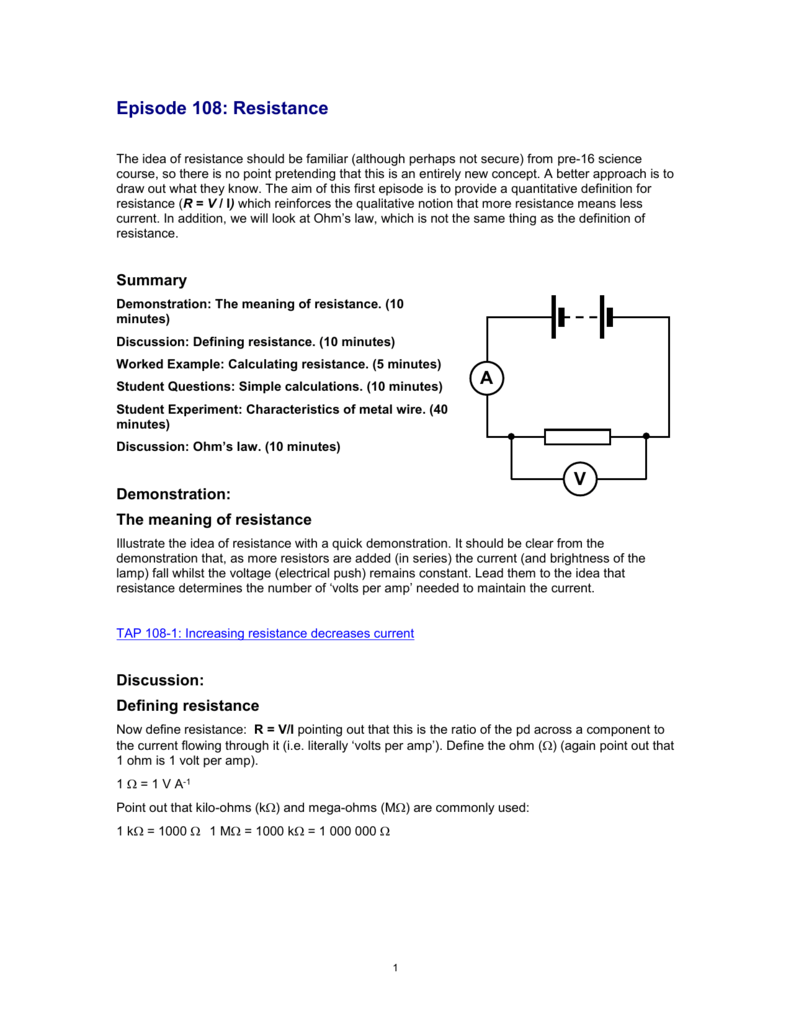



Resistance Teaching Advanced Physics




Ohm S Law




3 Ways To Read A Digital Ohm Meter Wikihow



How Voltage Current And Resistance Relate Ohm S Law



What Does Volts Amps Ohms And Watts Mean




How Does Electricity Work Ohm S Law Clearly Explained




Omega Symbol Sign And It S Meaning Greek Alphabet W W Ohm Symbol
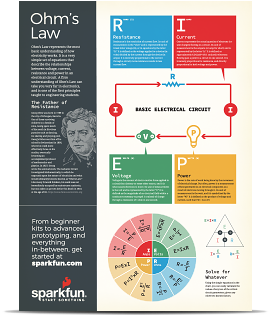



Voltage Current Resistance And Ohm S Law Learn Sparkfun Com




Relationship Between Voltage Current And Resistance
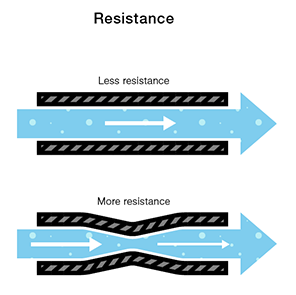



Voltage Current Resistance And Ohm S Law Learn Sparkfun Com




Ohm S Law Symbol Voltage Omega Peace Symbol Text Electrical Wires Cable Png Pngegg



Ohm S Law Calculation Calculator Calculate Power Formulas Mathematical Ohm S Law Pie Chart Electric Voltage Drop Electric Current Resistance Formula Watt S Law Emf Magic Triangle Equation Tip Online Voltage Volts Resitor Resistance Amps



Physics Tutorial Ohm S Law And The V I R Relationship
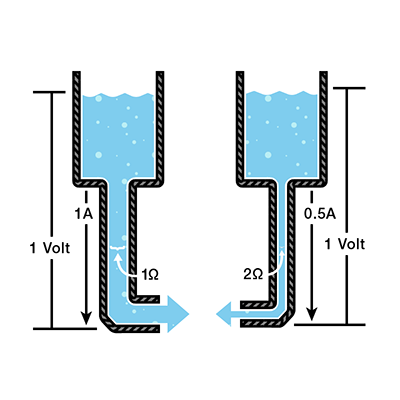



Voltage Current Resistance And Ohm S Law Learn Sparkfun Com




Electrical Power And Power Loss At Eclectic



Ohm S Law
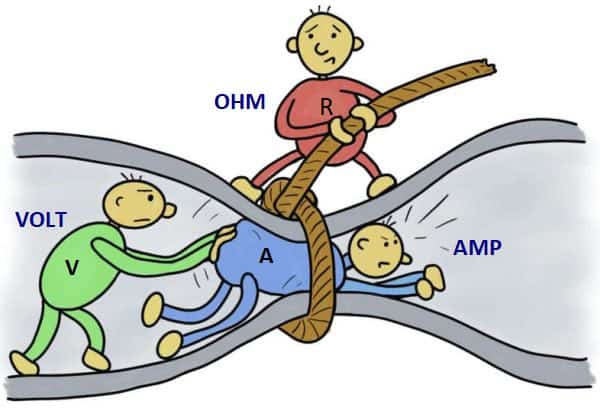



Ohm S Law Power And Energy Circuit Basics



Ohm S And Watt S Laws Spazztech




Ohm S Law Of Current Electricity Definition Limitations Videos Examples



How To Understand Electricity Volts Amps Watts And Electrical Appliances Dengarden




Electrical Resistance What Is It Symbol Formula Ac Vs Dc Resistance Electrical4u
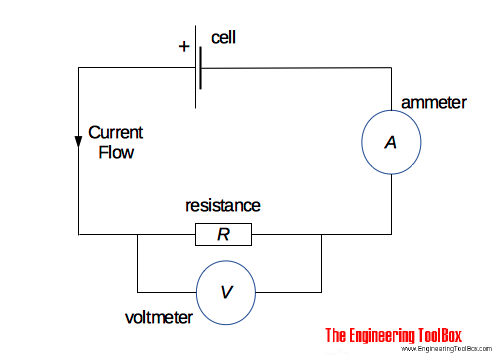



Electrical Units



Ohm Wikipedia



Ohm S And Watt S Laws Spazztech




Ohm S Law Flashcards Quizlet




Ohm S Law Essential Learning For Electricians




Ohm Wikipedia




Omega Symbol W W Meaning Alt Codes How To Write In All Devices
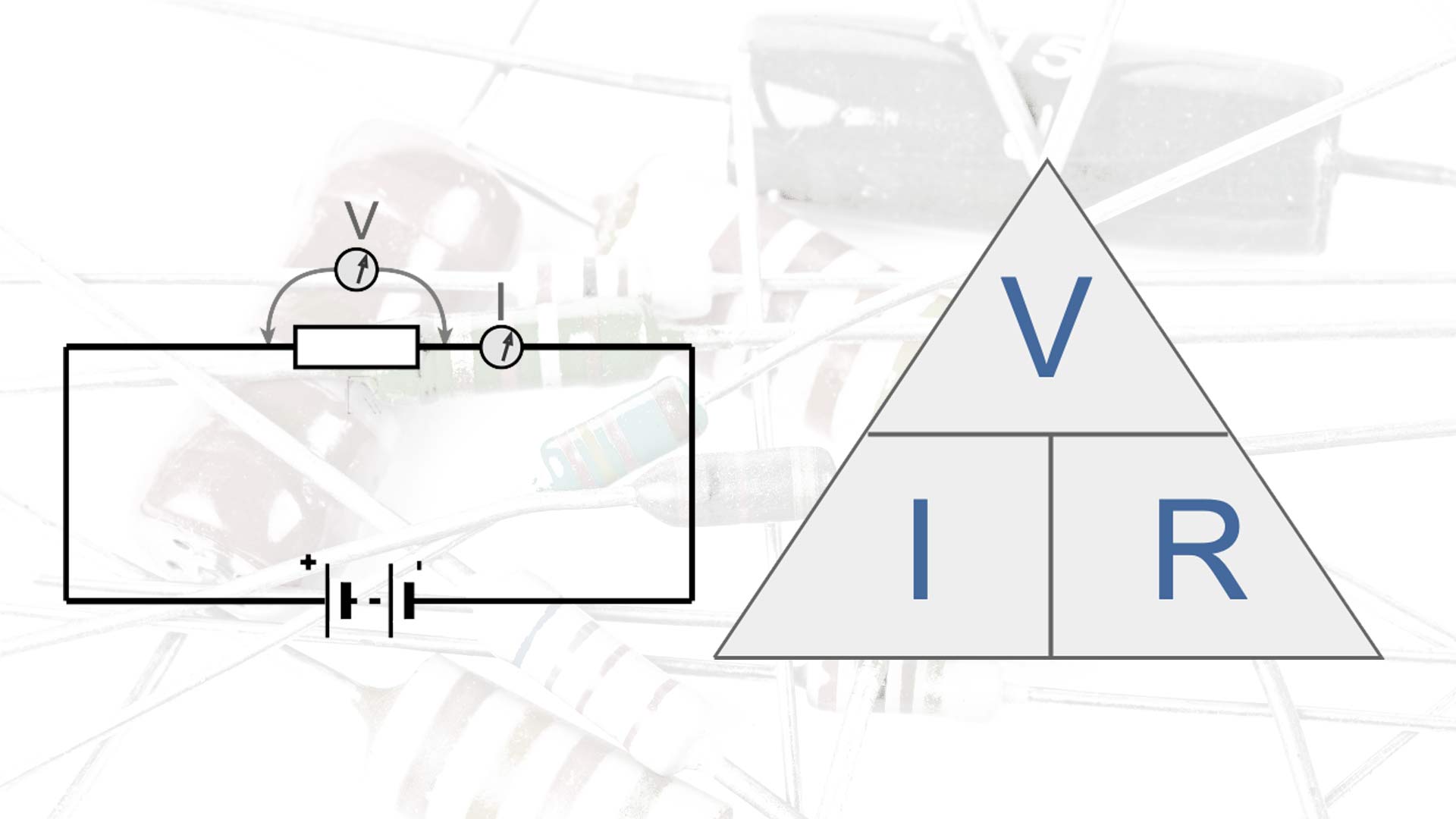



What Is Ohms Law Formula Equation Electronics Notes




Ohms Law Png Images Pngwing



Electric Current Ohm S Law




Ohm S Law The Engineering Mindset
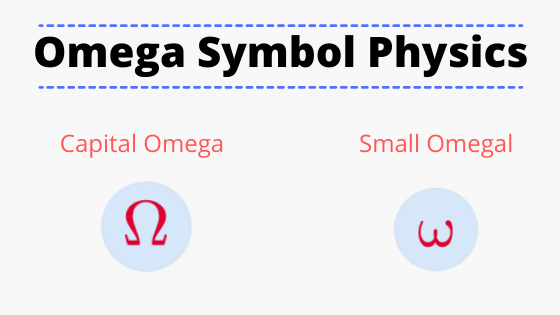



Omega Symbol Physics Uppercase And Lowercase Omega Symbol Meaning




Resistance Electronics Britannica



Ohm S Law For Beginners And Novices
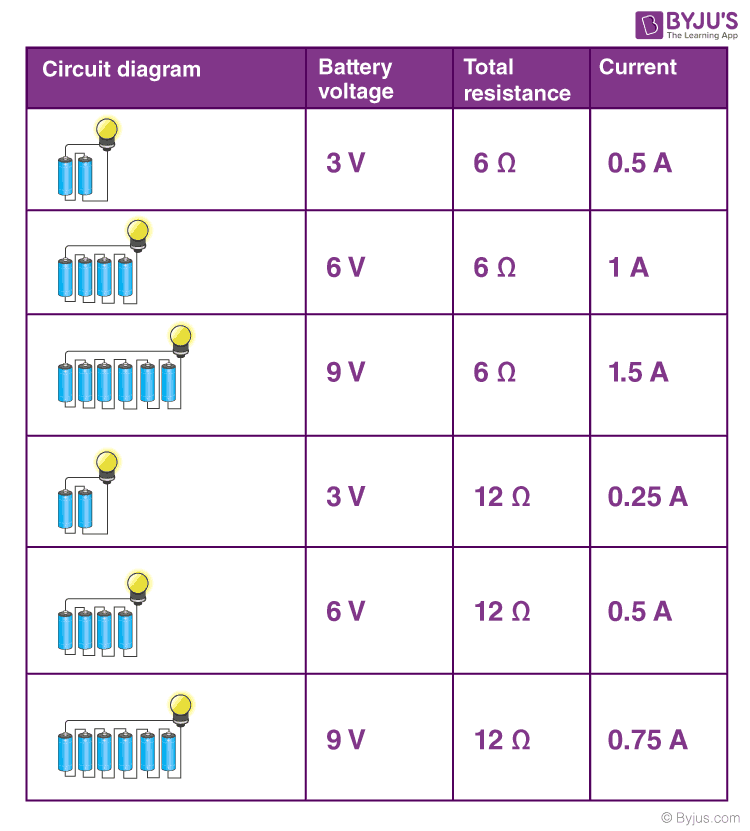



Ohm S Law Statement Formula Solved Examples Verification Faqs
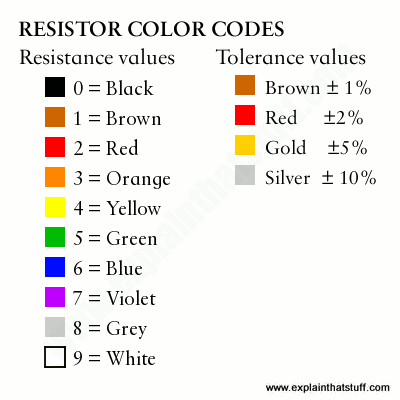



How Do Resistors Work What S Inside A Resistor
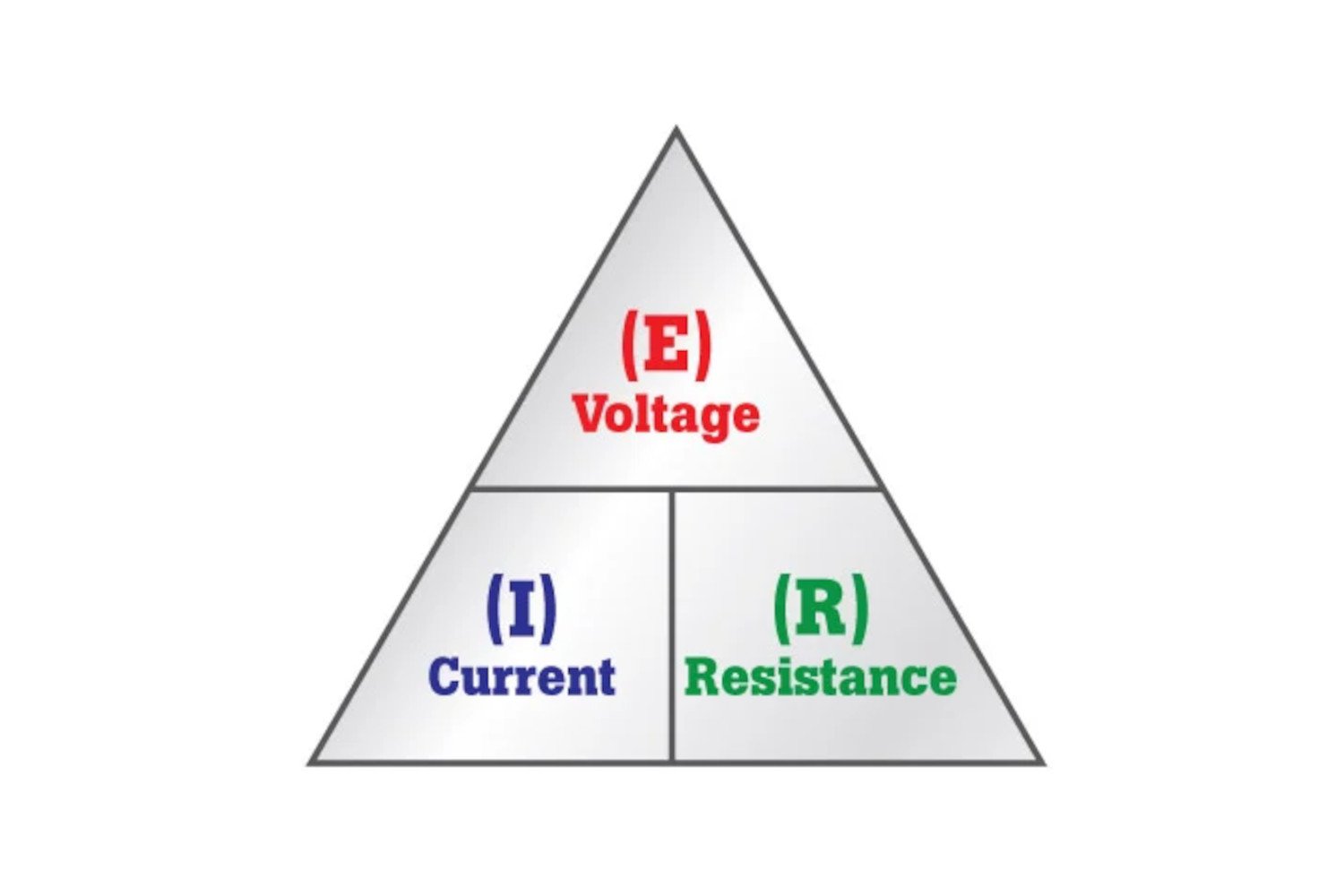



What Is Ohm S Law Fluke




Fundamentals Of Electronics
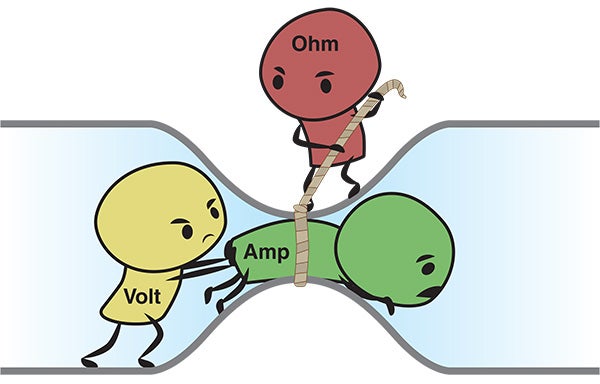



Ohms Law For Dummies 5 Steps Instructables
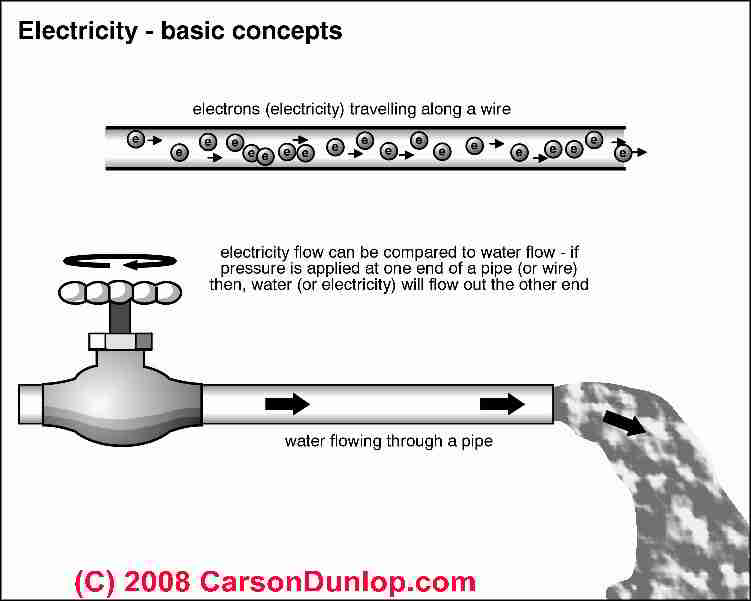



Definition Of Ohm S Law Explanation Measurement Of Electrical Resistance
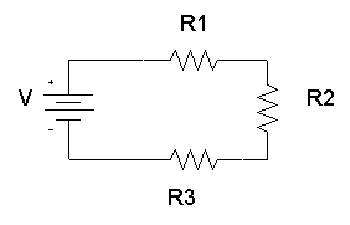



Electrical Resistance The Electricity Forum
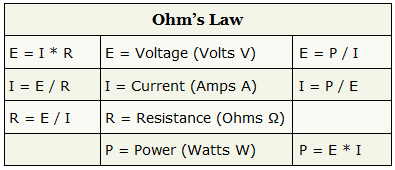



Ohms Law Electrical 101




Ohm S Law Definition Relationship Between Voltage Current Resistance Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Electricity Is Not Sorcery Isd Software Solutions




Q It E Qv Calculations Ohm S Law V Ir Investigating Factors Affecting Resistance I V Graph Characteristics Diode Ohmic Conductor Filament Lamp Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes




Basic Electricity Resistance And Ohm S Law Youtube



1




What Is Ohms Law Formula Equation Electronics Notes
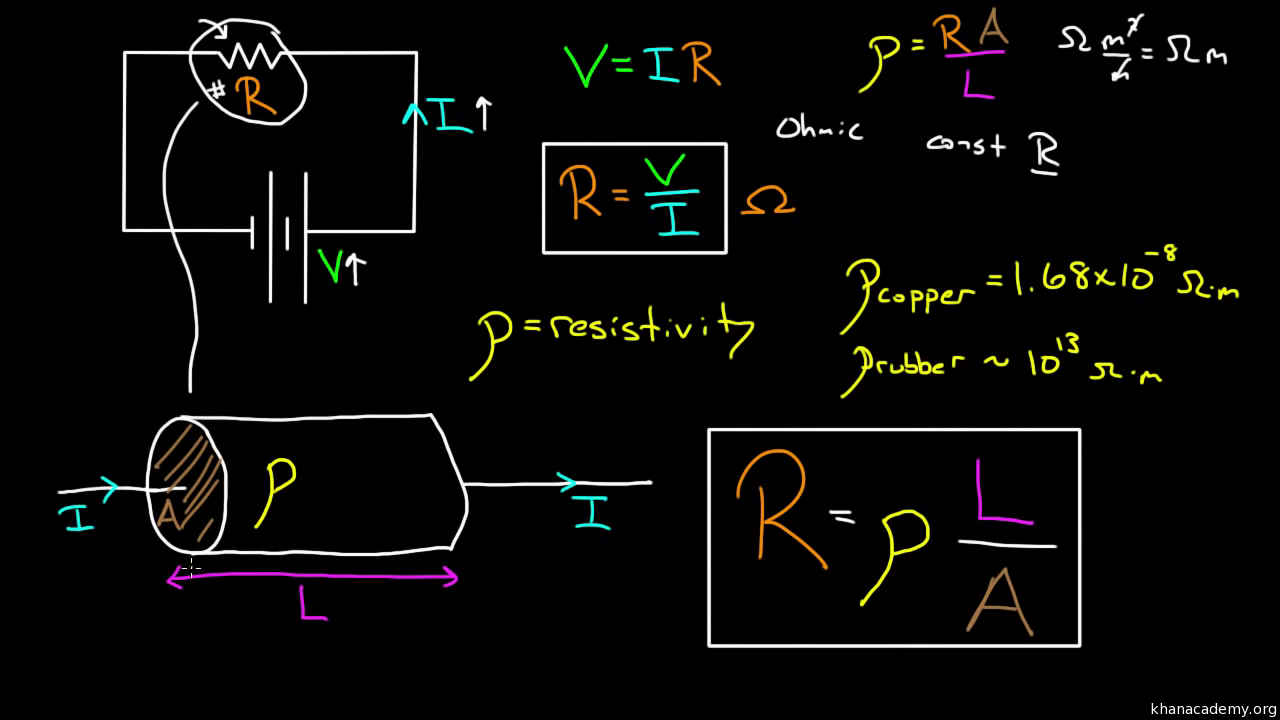



Resistivity And Conductivity Video Khan Academy



1




Resistance




Ohm Definition Formula Study Com
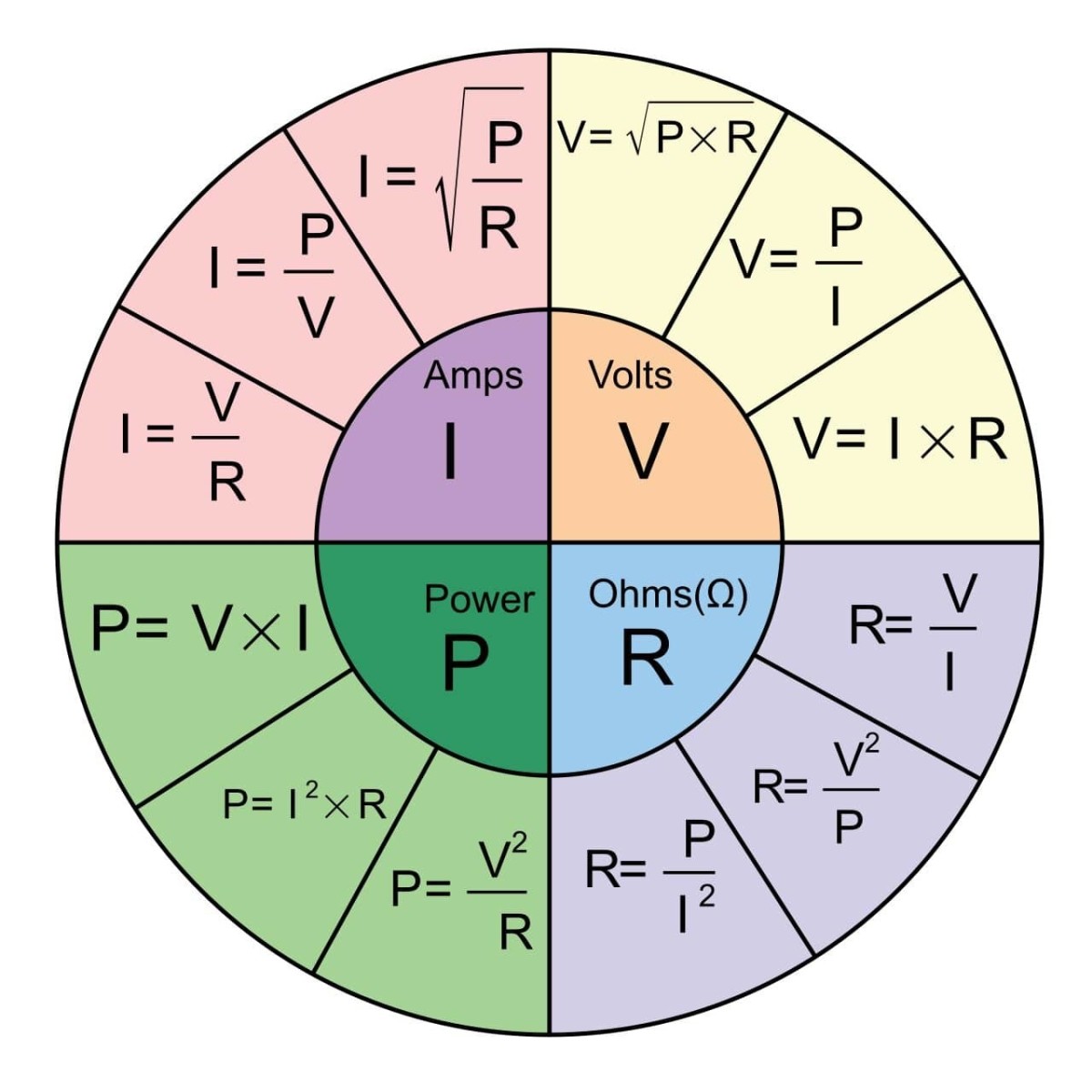



How To Understand Electricity Volts Amps Watts And Electrical Appliances Dengarden




Ohm S Law With Simple Explanation Examples




Ohm S Law Symbol Voltage Omega Peace Symbol Text Electrical Wires Cable Png Pngegg




Ohms Law An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
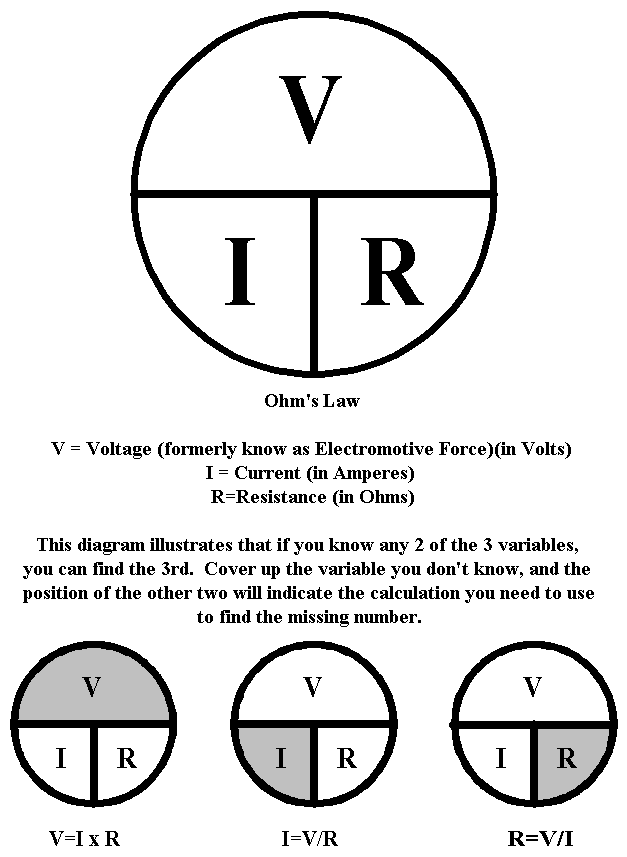



How Resistance Effects The Auto Electric System




Electrical Units And Metric Prefixes Examples




Resistance And Resistors Boundless Physics




W Wiktionary




Ohm S Law Wikipedia




How To Understand Electricity Watts Amps Volts And Ohms Owlcation
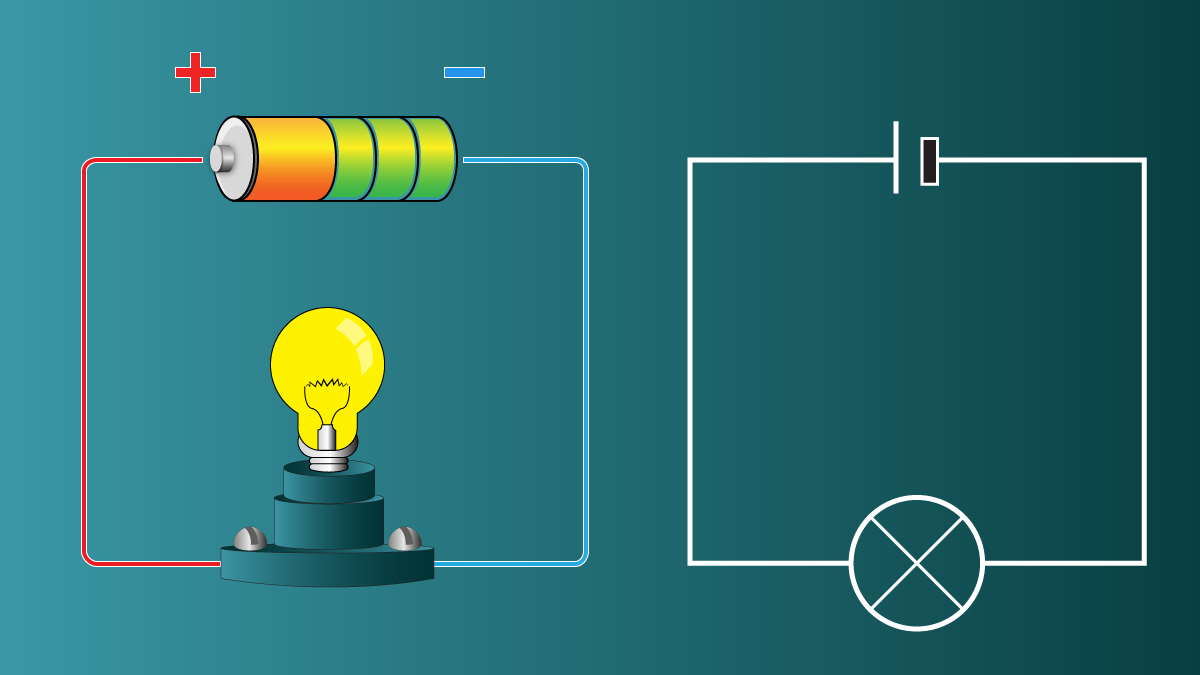



How To Understand Electricity Watts Amps Volts And Ohms Owlcation




What Is An Ohm With Pictures




Ohm S Law Statement Formula Solved Examples Verification Faqs




3 Ways To Read A Digital Ohm Meter Wikihow
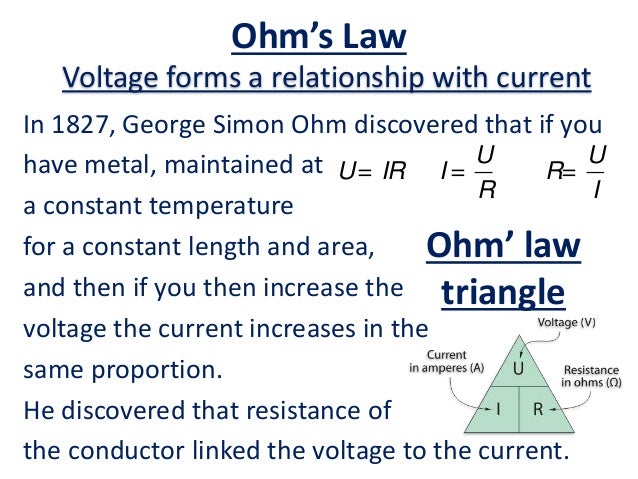



How Does Electricity Work Ohm S Law Clearly Explained



Understanding Ohm S Law Impedance And Electrical Phase 101 Audioholics
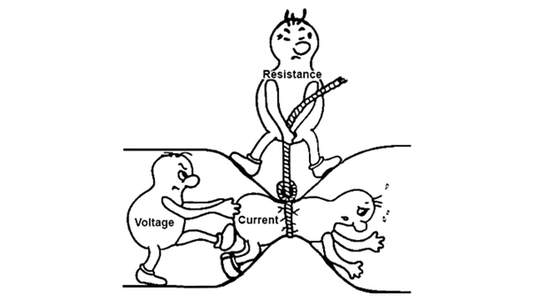



Ohms Law For Dummies 5 Steps Instructables



Ohm S Law Definition Formula Example Voltage Current And Resistance
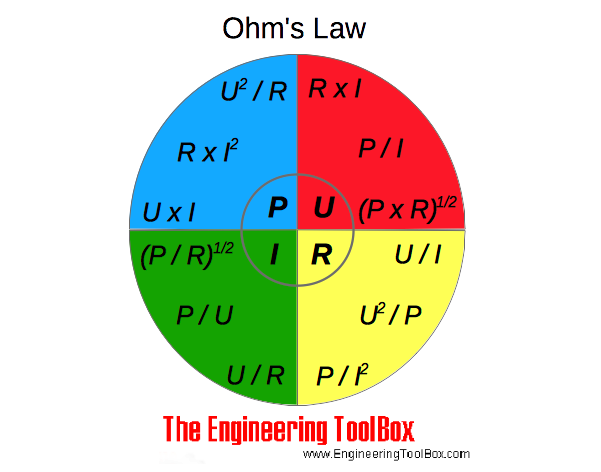



Ohm S Law



Physics Tutorial Ohm S Law And The V I R Relationship




Ohms Law Png Images Pngwing



Chapter 3 Basic Electronics



1




What Is Ohm S Law And How Does It Apply To Thermal Systems Watlow




Introduction To Circuits And Ohm S Law Video Khan Academy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿